Learning occurs in the field of attention (not necessarily the same as concentration or even conscious awareness). Learning is a process of connecting, integrating, and incorporating new experiences. Learning involves co-implicating new interrelationships between the memory of previous experiences and the living ‘edge of now’ being experienced (attention-differentiation-disambiguation). As sensory and cognitive processes provide foreground input to the stream of attention they also trigger re-membering into the stream (according to emotional and cognitive associative processes) relevant short and long-term memories. This dynamic inner co-assembling of memories provides the background flow, the interior context, and the populates of working memory within which learning occurs. The foreground and background processes are concurring real-time within attention and move through a cyclic process of coherence, dissonance, differentiation, disambiguation, co-implication, and renewed coherence. Between the flowing stream of meanings emerging from the foreground and the stream of background meanings arising in a wake-like response, new learning occurs.
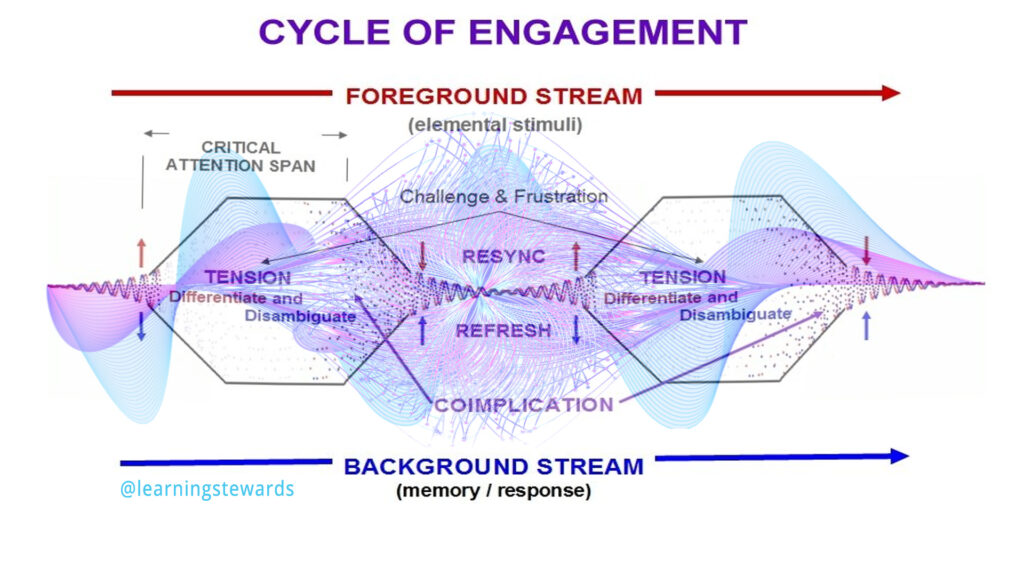
The critical aspect of this inner relationship among processes is that attention must span and provide the ‘field’ this cycle takes place in. If the span of attention is inadequate for the stretch between foreground and background, the learner disengages. A learner’s capacity for attentional stretch depends on having enough (affective) interest to sustain continuity through any stutters or other attentional disruptions (whether cognitive or affective) experienced in the stretching.
Learning extends our presence by differentiating and disambiguating the live stream of experiencing and creatively co-implicating its meaning with meanings previously learned.
Disengagement from learning results when the foreground stretches too far or long away from relevancy or when the emotions aroused stutter or break the flow of attentional interest. However, disengagement is avoidable when it is caused by extraneous ambiguities (confusion) introduced by the form, structure, or pacing of information intended to be facilitative (i.e., language, vocabulary, conceptual density, explication style, complexity level, pace, etc…) and/or when it causes disruptive emotional reactions to the feeling of the learning challenge (downward spiral of shame)
See “Nintendo Studies” in “From Here to Implicity” article (1990) for the genesis of these conceptions.
PLEASE… We can’t sustain our efforts without your help. If you think we are on the right track, or even one that should be given consideration, then please help us. Please forward our posts as widely as you can. Your help can make a big difference in whether our work succeeds. Thank you.

[…] ادامه مطلب […]
[…] Cycle of Engagement […]
[…] Cycle of Engagement […]
[…] Cycle of Engagement […]